As a Seller How Do You Know Letter of Credit Is Not Counterfeit in International Trade
Don't lose potential concern to competitors past overlooking different payment options which could be bonny to your international buyer. Explore several payment methods and notice the i best suited to your needs.
Many American businesses new to selling U.S. products overseas expect or prefer to exist paid in full in advance. While in that location is zero risk of non-payment if you do business this mode, y'all take chances losing business by overlooking competitors willing to offer buyers better payment options. Consider more bonny payment methods as outlined in this article and accompanying videos.
Methods of Payment
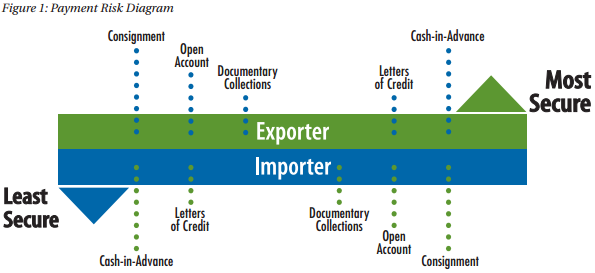
To succeed in today's global marketplace and win sales against foreign competitors, exporters must offer their customers attractive sales terms supported past the appropriate payment methods. Because getting paid in full and on fourth dimension is the ultimate goal for each export sale, an appropriate payment method must be chosen carefully to minimize the payment risk while also accommodating the needs of the buyer. As shown in effigy one, there are five primary methods of payment for international transactions. During or before contract negotiations, you should consider which method in the effigy is mutually desirable for y'all and your customer.
Key Points
- International trade presents a spectrum of adventure, which causes uncertainty over the timing of payments between the exporter (seller) and importer (foreign buyer).
- For exporters, whatsoever sale is a gift until payment is received.
- Therefore, exporters want to receive payment as soon equally possible, preferably as soon as an society is placed or before the goods are sent to the importer.
- For importers, any payment is a donation until the appurtenances are received.
- Therefore, importers want to receive the goods as soon as possible simply to filibuster payment equally long as possible, preferably until subsequently the appurtenances are resold to generate enough income to pay the exporter.
Greenbacks-in-Advance
With greenbacks-in-advance payment terms, an exporter can avoid credit risk because payment is received before the buying of the goods is transferred. For international sales, wire transfers and credit cards are the most commonly used cash-in-advance options bachelor to exporters. With the advancement of the Internet, escrow services are becoming another cash-in-advance option for small export transactions. However, requiring payment in advance is the least attractive selection for the buyer, considering information technology creates unfavorable cash menstruation. Foreign buyers are too concerned that the goods may not exist sent if payment is fabricated in advance. Thus, exporters who insist on this payment method as their sole manner of doing business may lose to competitors who offer more attractive payment terms. Larn more than almost Cash-in-Advance.
Letters of Credit
Letters of credit (LCs) are i of the most secure instruments available to international traders. An LC is a commitment by a banking concern on behalf of the buyer that payment will exist fabricated to the exporter, provided that the terms and conditions stated in the LC have been met, as verified through the presentation of all required documents. The buyer establishes credit and pays his or her bank to render this service. An LC is useful when reliable credit information almost a foreign heir-apparent is difficult to obtain, only the exporter is satisfied with the creditworthiness of the buyer's foreign bank. An LC likewise protects the buyer since no payment obligation arises until the goods take been shipped as promised. Learn more than about Letters of Credit.
Documentary Collections
A documentary drove (D/C) is a transaction whereby the exporter entrusts the collection of the payment for a sale to its banking company (remitting bank), which sends the documents that its buyer needs to the importer's banking concern (collecting bank), with instructions to release the documents to the buyer for payment. Funds are received from the importer and remitted to the exporter through the banks involved in the collection in commutation for those documents. D/Cs involve using a draft that requires the importer to pay the face amount either at sight (certificate against payment) or on a specified date (document against acceptance). The collection letter gives instructions that specify the documents required for the transfer of championship to the goods. Although banks practice human activity as facilitators for their clients, D/Cs offer no verification process and express recourse in the upshot of not-payment. D/Cs are generally less expensive than LCs. Learn more about Documentary Collections.
Open Account
An open account transaction is a auction where the goods are shipped and delivered before payment is due, which in international sales is typically in 30, 60 or 90 days. Obviously, this is one of the most advantageous options to the importer in terms of greenbacks flow and toll, but it is consequently 1 of the highest risk options for an exporter. Because of intense competition in consign markets, strange buyers often printing exporters for open account terms since the extension of credit past the seller to the buyer is more mutual abroad. Therefore, exporters who are reluctant to extend credit may lose a sale to their competitors. Exporters tin can offer competitive open up business relationship terms while substantially mitigating the chance of not-payment by using one or more of the appropriate trade finance techniques covered later in this Guide. When offering open account terms, the exporter tin seek extra protection using export credit insurance.
Assignment
Consignment in international trade is a variation of open account in which payment is sent to the exporter just subsequently the appurtenances accept been sold by the strange distributor to the stop client. An international consignment transaction is based on a contractual organization in which the foreign distributor receives, manages, and sells the goods for the exporter who retains title to the appurtenances until they are sold. Clearly, exporting on assignment is very risky as the exporter is not guaranteed any payment and its goods are in a foreign country in the hands of an independent distributor or agent. Assignment helps exporters become more competitive on the basis of ameliorate availability and faster commitment of goods. Selling on consignment can likewise help exporters reduce the directly costs of storing and managing inventory. The cardinal to success in exporting on assignment is to partner with a reputable and trustworthy foreign distributor or a third-political party logistics provider. Appropriate insurance should be in place to cover consigned appurtenances in transit or in possession of a strange benefactor as well as to mitigate the chance of not-payment.
kershawstareer1949.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.trade.gov/methods-payment
0 Response to "As a Seller How Do You Know Letter of Credit Is Not Counterfeit in International Trade"
Post a Comment